Magnitude 2 Earthquake Strikes Near Nikiski, Alaska
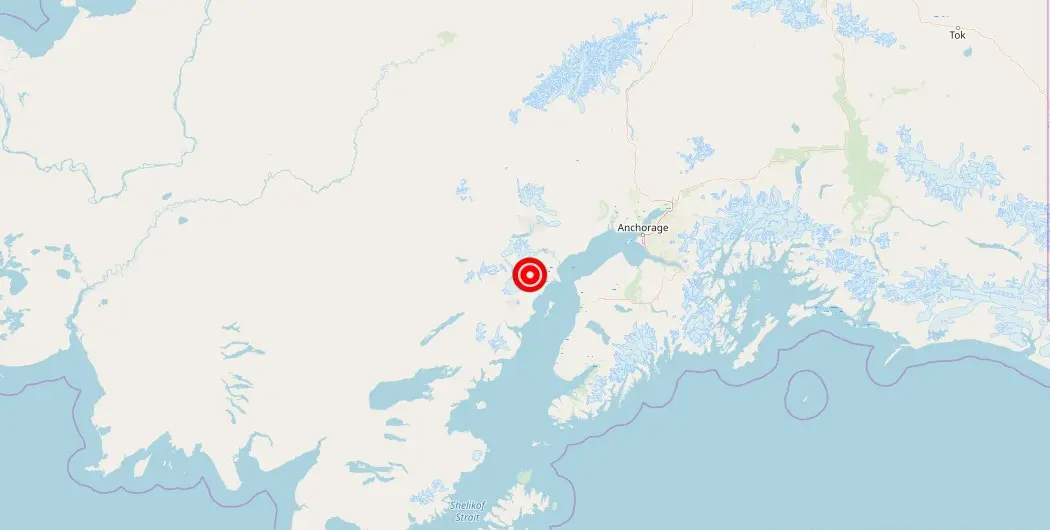
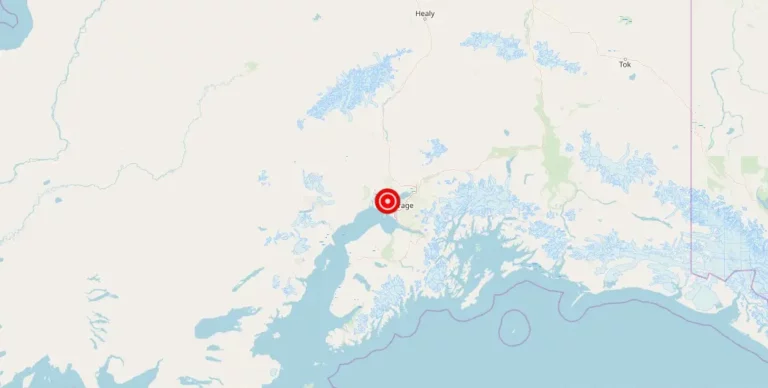
On Wednesday, March 15, a magnitude 2 earthquake occurred 60 kilometers west of Nikiski, Alaska. While a magnitude 2 earthquake is considered minor, it still has the potential to cause minimal damage and shake things up in the surrounding areas. The location of the earthquake, however, is noteworthy as Nikiski is a small community located on the Kenai Peninsula in south-central Alaska.
Exploring the Region Affected by the Recent Alaska Earthquake

The region 60 km west of Nikiski, Alaska is part of the Cook Inlet region, a major subduction zone where the North American Plate meets the Pacific Plate. This area is known for its high level of seismic activity and is considered to be one of the most seismically active regions in Alaska. It has experienced several large earthquakes and aftershocks in the past, the most notable being the 1964 Great Alaska earthquake, which had a magnitude of 9.2 and caused widespread damage and loss of life. Due to its location, the region is also at risk for tsunamis, which can be triggered by large earthquakes or landslides. As a result of the high seismic activity, the region is closely monitored by various seismological organizations to help mitigate the potential impacts of future seismic events.
Potential Hazards and Future Risks for Nikiski, Alaska after Earthquake
In Nikiski, Alaska, the recent earthquake has left a high likelihood of several potential hazards and dangers after the catastrophic event. It’s important to remain vigilant and aware of these risks and take necessary precautions, as well as prepare for future seismic activity.
The earthquake could cause significant property damage to buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructure, imposing a financial burden on the people living in the region. The danger of landslides, rockfalls, and possible new fault openings in the aftermath of the event puts the area at risk for mudflows and debris flow. Such situations could also damage or wipe away existing infrastructure, obstructing transportation and commerce through the industrial area.
The earthquake can also cause long-term environmental impacts, such as ground subsidence or contamination of the water supply as a result of soil alteration, which significantly affects crucial everyday services like drinking water and drainage systems. Tsunami triggered by the earthquake could cause flooding, particularly in coastal locations, impairing both personal property and crops.
Governmental agencies, emergency services, and other organizations have taken measures to mitigate the effects of the earthquake. Nevertheless, it’s crucial to stay informed, review emergency plans, and follow advice from official sources to prevent injury, loss of life or property, or even business disruption, particularly in such an industrial area. It’s important to prepare for future emergencies to prevent any potential harm that could arise due to seismic or other forms of environmental catastrophes.
Resources for Those Affected by Earthquake in Nikiski, Alaska
- Alaska Earthquake Center – provides information on recent earthquakes in Alaska, including maps, seismic data, and other resources.
- Alaska Division of Homeland Security and Emergency Management – responsible for coordinating the state’s response to disasters and emergencies.
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) – provides a range of resources for disaster response, including assistance for individuals and businesses affected by earthquakes.
- The American Red Cross – provides shelter, food, mental health services, and other resources for disaster victims.
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS) – provides real-time earthquake monitoring and data collection.
- The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – provides tsunami alerts and warning systems for coastal areas.