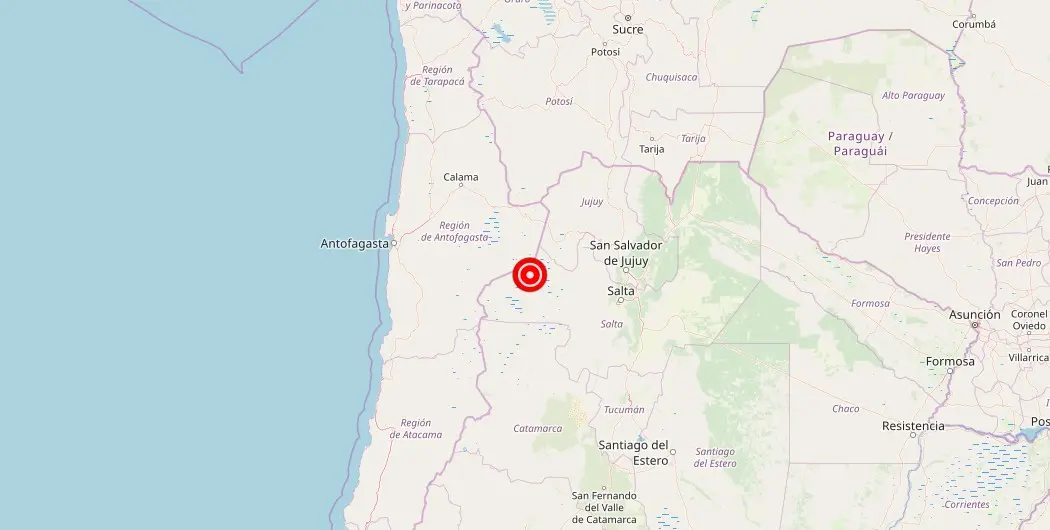
Magnitude 4.30 Earthquake Strikes Near Chile-Argentina Border Region, La
Breaking News: Powerful Earthquake Strikes Chile-Argentina Border Region
In a stunning display of nature’s might, a powerful earthquake has just rocked the Argentine side of the Chile-Argentina border region. Today, on Saturday, August 19, an event of seismic proportions unfolded, sending shockwaves across the land and leaving observers in awe of this relentless force of nature. The magnitude of the earthquake, yet to be fully determined, has struck fear and curiosity into the hearts of millions of people residing in this densely populated area. As we await more detailed information, it becomes increasingly imperative to grasp the significance of this event, with its potential ramifications reverberating far and wide. Stay tuned for further updates on this seismic incident, as our team diligently uncovers crucial details about the aftermath and potential consequences.
Earthquake Strikes the Chile-Argentina Border Region of La: Exploring the Geography and Historical Significance

The Pacific Ring of Fire is a vast region characterized by high seismic activity, primarily encompassing the edges of the Pacific Ocean. It is outlined by a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, volcanic belts, plate movements, and volcanic activity. This region is notorious for its frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, making it one of the most seismically active areas on Earth.
The Pacific Ring of Fire spans approximately 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles) and is home to about 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. It stretches from the coasts of North and South America, including the west coast of the United States, along the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, across the Pacific to Asia, including Japan, the Philippines, and Indonesia, and down to New Zealand. The entire western coast of North America, from California to Alaska, lies within this seismic belt.
The region’s seismic activity is primarily caused by the intense tectonic plate movements occurring as several large plates, including the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, Philippine Sea Plate, and others, interact with one another. These interactions result in subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath another, creating deep trenches, and immense pressure builds up along the fault lines. This accumulated energy is eventually released in the form of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
The Ring of Fire accounts for approximately 90% of the world’s earthquakes, both major and minor. Some of the most devastating earthquakes in history have occurred in this area, such as the Great Chilean earthquake in 1960, the largest earthquake ever recorded, the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, and the Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan in 2011.
Volcanic eruptions are also frequent in the Pacific Ring of Fire due to the subduction zones and the presence of magma chambers beneath the Earth’s surface. Some noteworthy volcanic eruptions include the eruptions of Mount Saint Helens in Washington state, USA, in 1980, Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, and Mount Merapi in Indonesia in recent decades.
The high seismic and volcanic activity in the Pacific Ring of Fire poses significant threats to human populations living in the surrounding areas. Governments and scientific institutions closely monitor the region and implement measures to mitigate the risks associated with earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Potential Hazards and Dangers: Earthquake near Chile-Argentina Border in La – Future Risks and Key Information
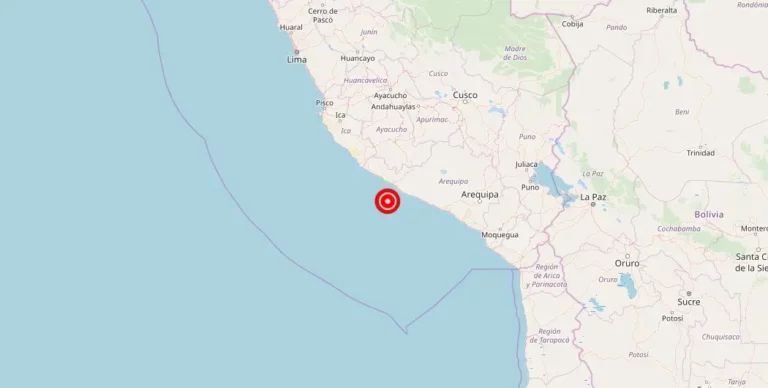
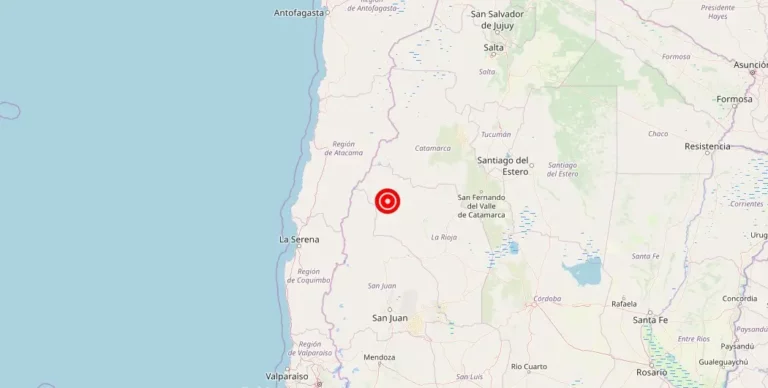
An earthquake with a magnitude struck the Argentine side of the Chile-Argentina border region, La, recently. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the earthquake had a low magnitude and occurred in the San Francisco area.
Thankfully, there are currently no reports of damage, injuries, or other impacts resulting from the earthquake. Despite this, its tremors were felt across the city, although its impact remained limited due to its low magnitude.
The USGS affirms that earthquakes with magnitudes below 3.0 are typically not felt by people and cause little to no damage. However, events like these often serve as reminders to stay prepared for larger earthquakes that may occur in the future. It is crucial to be aware and take necessary precautions to mitigate potential risks associated with such natural disasters.
As of now, there are no further updates or reports regarding the recent earthquake in the Argentine side of the Chile-Argentina border region, La. Authorities continue to monitor the situation closely and will provide additional information as it becomes available.
It is important for residents in the area to remain vigilant and to adhere to any guidance or alerts issued by local authorities. Being prepared for the possibility of future earthquakes can save lives and minimize the impact of such events.
It is advisable for residents to have emergency kits readily available, including essential supplies such as food, water, and first aid items. Creating an emergency plan with family members and knowing evacuation routes and safe zones can also be instrumental in ensuring everyone’s safety.
While this recent earthquake did not result in any significant damage or casualties, it is always a timely reminder to prioritize preparedness and resilience in the face of natural disasters.
Earthquake Resources for Chile-Argentina Border Region
- Chilean Ministry of the Interior and Public Security: Official government website providing updates on the earthquake, emergency contacts, and information about ongoing relief efforts.
- Argentinian Ministry of Security: Official government website offering news, emergency numbers, and resources for those affected by the earthquake in the Argentine side of the border region.
- US Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS earthquake hazards program provides real-time earthquake information and resources for affected areas, including maps, data, and safety guidelines.
- FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency): FEMA provides disaster response and recovery resources, including guidance on emergency preparedness, assistance programs, and information on how to apply for aid.
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies: The international humanitarian organization’s website offers information on local branches providing emergency services, medical aid, and support for affected communities.
- Pacific Tsunami Warning Center: The PTWC monitors seismic activity and issues tsunami warnings for the Pacific Ocean. They provide updates on potential tsunami threats in the aftermath of an earthquake.
- National Earthquake Information Center (NEIC): A division of the USGS, the NEIC gathers and analyzes earthquake data from around the world and provides information on recent seismic activity.
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO): The PAHO website offers guidance on post-earthquake health concerns, including injury prevention, access to medical care, and disease control in affected areas.
- Local News Websites: Local news outlets may provide valuable updates, news reports, and community resources specific to the affected region. Check for reliable news sources such as national newspapers, TV channels, or radio stations.
- Shelter and Relief Organizations: Research local and international non-profit organizations involved in disaster relief and recovery efforts. These organizations can provide temporary shelter, supplies, and other assistance to affected individuals and communities.