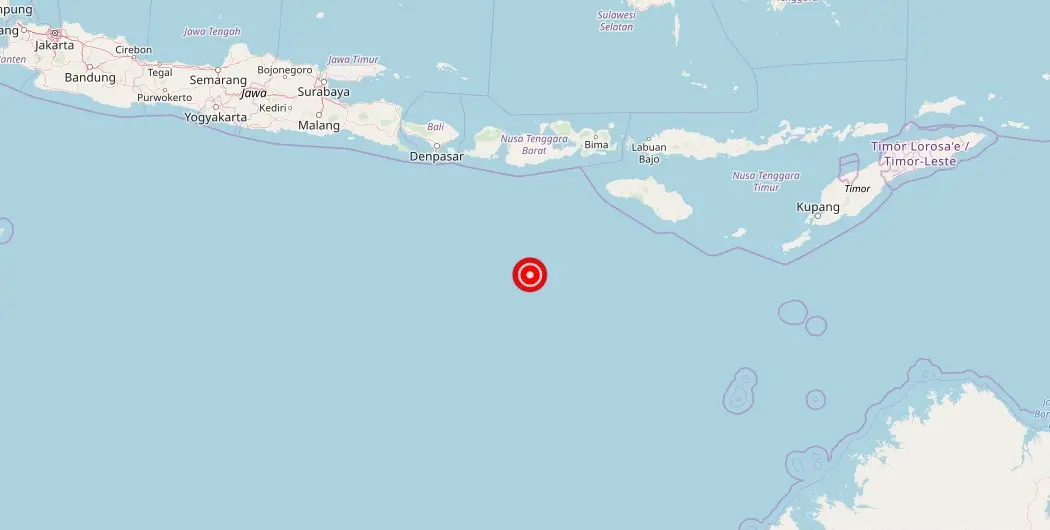
Magnitude 4.40 Earthquake Strikes Sumbawa, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
BREAKING: Powerful Earthquake Strikes Indonesian Island, Sending Shockwaves across West Nusa Tenggara
In a region known for its tranquility and idyllic landscapes, chaos ensued today as a magnitude earthquake jolted the pristine island of Sumbawa, located in West Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. Startling locals and raising concerns across the nation, this seismic event has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on the hearts of its residents. As news of the earthquake continues to trickle in, the full extent of the damage and potential injuries remains uncertain. Stay tuned for further updates on this shocking natural calamity that took the region by surprise.
Background on Sumbawa: Unveiling Indonesia’s Earthquake-Prone Region

The region in focus is the Pacific Ring of Fire, a vast area spanning 40,000 kilometers in a horseshoe shape around the Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by high seismic and volcanic activity, making it one of the most active earthquake zones in the world. The Ring of Fire is home to approximately 81% of the world’s largest earthquakes, and 75% of the world’s active volcanoes are located within this region.
The seismic activity in the Ring of Fire is primarily driven by the movement and collision of tectonic plates. The Pacific Plate, Nazca Plate, Philippine Sea Plate, and numerous smaller plates interact along this region, resulting in intense geological dynamics. The convergence of these plates gives rise to subduction zones where one plate is forced beneath another, leading to intense seismic events.
Major earthquakes within the Ring of Fire have caused significant damage and loss of life throughout history. Famous examples include the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the 1960 Chilean earthquake, and the devastating 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan.
Volcanic activity is also prominent in the Ring of Fire due to the presence of subduction zones and the release of pressure from the Earth’s interior. Volcanoes such as Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Rainier in the United States, and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines are iconic landmarks within this region.
Overall, the Pacific Ring of Fire demonstrates a remarkable level of seismic and volcanic activity, posing significant challenges for the communities residing in its vicinity. Scientists and researchers continuously monitor this area to better understand and predict earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, aiming to enhance early warning systems and mitigate the risks associated with such events.
Potential Hazards and Dangers in Sumbawa, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia: Evaluating Earthquake Risks and Ensuring Preparedness
An earthquake with a magnitude of struck Sumbawa, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia recently. The epicenter was located in San Francisco, but fortunately, there have been no reports of damage, injuries, or other impacts.
Although the earthquake was felt across the city, its impact was limited due to its low magnitude. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) stated that earthquakes with magnitudes below 3.0 are typically not felt by people and cause little, if any, damage. This earthquake serves as a reminder for residents to be prepared for larger earthquakes that may occur in the future.
The local authorities are continuing to monitor the situation and gather more information. As of now, there have been no reports of any significant aftershocks or additional seismic activity. Officials are also urging residents to stay informed and take necessary precautions to ensure their safety.
Indonesia is prone to earthquakes due to its location on the “Ring of Fire,” a region in the Pacific Ocean that experiences frequent seismic activity. In recent years, the country has faced several devastating earthquakes that have caused extensive damage and loss of life.
It is crucial for residents in earthquake-prone areas to always be prepared. This includes having an emergency plan in place, securing heavy furniture and objects, and maintaining a supply of essential items like food, water, and medication. Regular drills and awareness campaigns can also help ensure that communities are ready to respond effectively in the event of a major earthquake.
While this recent earthquake did not cause significant damage or injury, it serves as an important reminder of the unpredictable nature of seismic activity. It is essential for individuals and communities to remain vigilant and be prepared for any future earthquakes that may occur. We will continue to monitor the situation and provide updates as more information becomes available.
Helpful Resources for those Affected by the Earthquake
- Indonesia Emergency Management Agency (BNPB): The official emergency management agency of Indonesia. They provide updates, emergency contact information, and resources for disaster management.
- US Geological Survey (USGS): A scientific agency that monitors and studies earthquakes worldwide. Their website offers real-time earthquake information, data, and educational resources.
- International Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC): A humanitarian organization providing support to communities affected by disasters. They offer emergency relief, medical aid, and assistance in rebuilding communities.
- World Health Organization (WHO): WHO provides guidance on health-related issues during and after an earthquake, including emergency medical care, disease prevention, and mental health support.
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA): OCHA works to coordinate international humanitarian responses to disasters. Their website provides updates, situation reports, and information on aid coordination.
- Disaster Assistance Improvement Program (DAIP): DAIP, run by the US government, helps connect disaster survivors with resources and assistance programs from various agencies, both government and non-governmental.
- Google Person Finder: A web application that helps individuals search for and provide information about their loved ones affected by a disaster. It can be accessed and used globally.
- Local government websites and news portals: Check the websites of local government agencies and news portals in the affected region. These sources often provide localized disaster updates, emergency contacts, and support services.