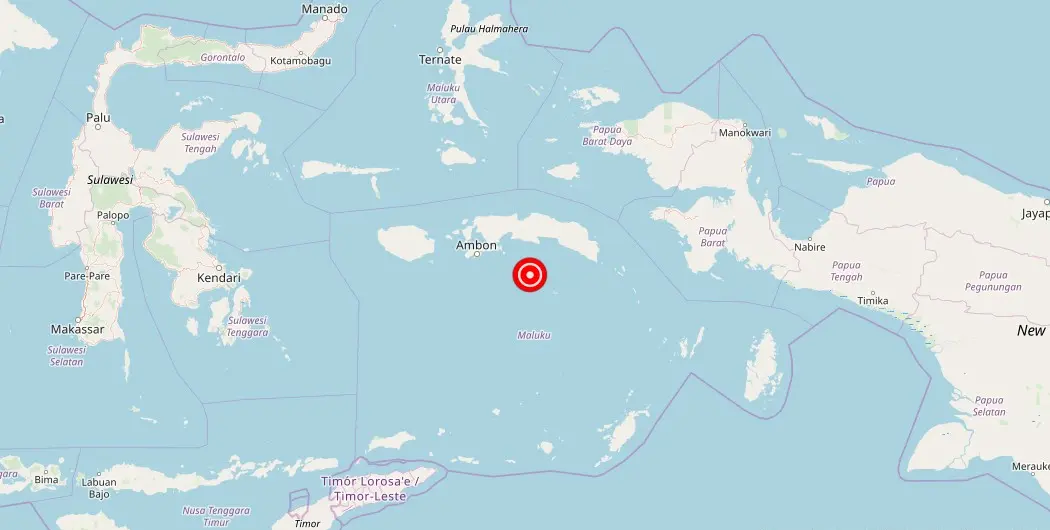
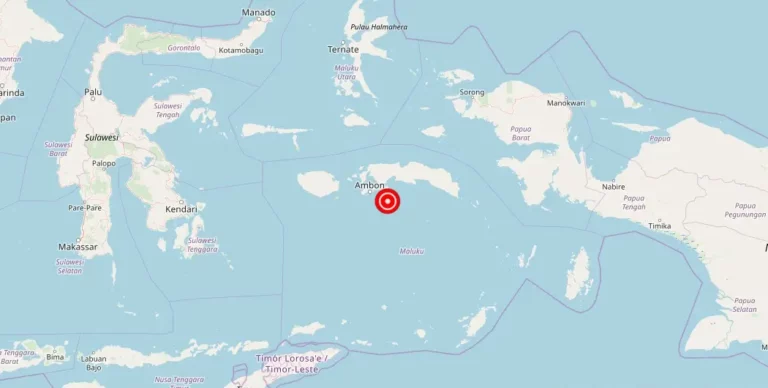
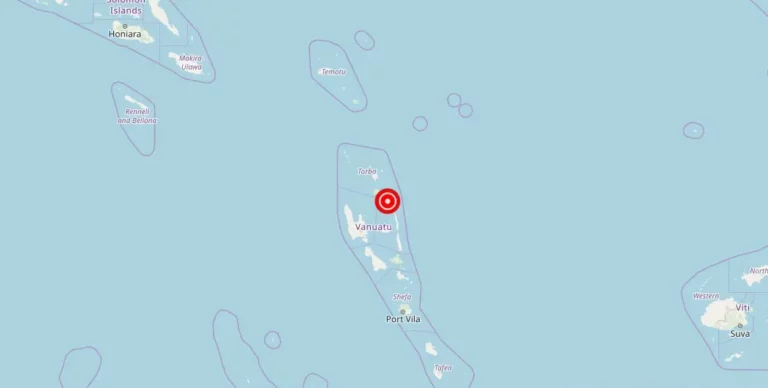
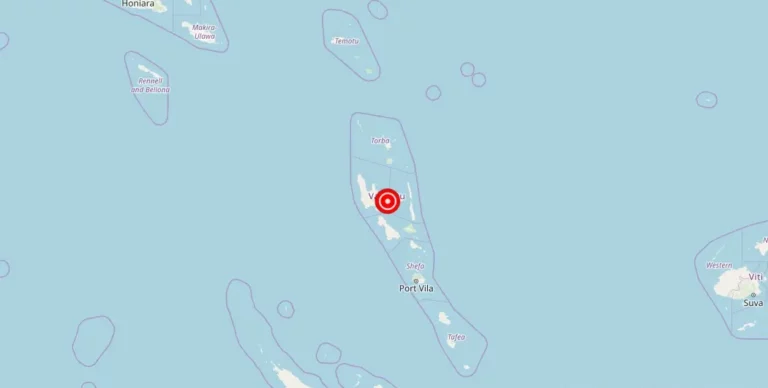
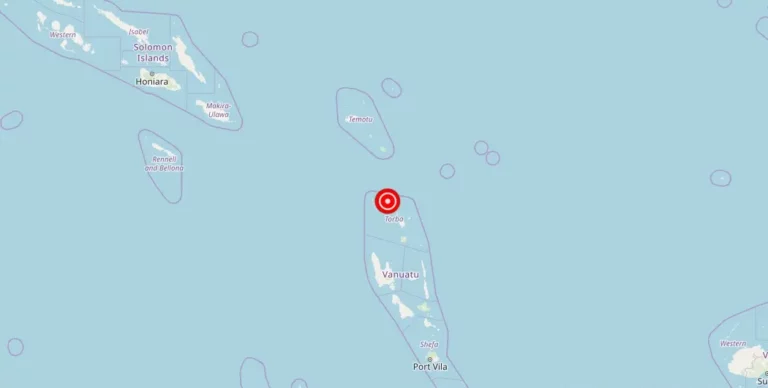
Magnitude 4.60 earthquake strikes near Amahai, Maluku, Indonesia
BREAKING NEWS: Earthquake Strikes Island Paradise, Awakens Fears and Raises Questions
In a heart-stopping moment, the tranquil island of Amahai, nestled amidst the breathtaking vistas of Maluku, Indonesia, was shaken to its core today. A powerful earthquake, with magnitude yet to be ascertained, struck this idyllic coastal region, sending shockwaves through the entire nation. As the ground trembled ominously, questions and concerns surged like wildfire. With its stunning landscapes and rich cultural heritage, Amahai, known as a paradise on earth, now finds itself at the epicenter of an event that could have far-reaching repercussions. Tantalizingly, as information emerges in dribs and drabs, the gravity of the situation remains uncertain, leaving us grasping for updates and praying for the safety of all those who call this haven their home.
Note: For the most up-to-date information, stay tuned to our news channel and our website as further updates on this developing situation become available.
Background Information: Amahai, Maluku – A Region Rich in Cultural Heritage and Natural Wonders

The region in focus is located along the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for its intense seismic activity. This region lies on the western coast of North America, encompassing parts of Alaska and California, along with several other states. It is a highly seismically active region due to the presence of multiple tectonic plate boundaries.
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a major area of tectonic plate convergence, where several plates interact with each other. Specifically, the North American, Pacific, and Juan de Fuca plates, among others, all converge in this region, creating a complex and dynamic system. The frequent interactions between the plates result in high seismic activity, including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
The region experiences a wide range of earthquakes, varying in magnitude and frequency. Both subduction and transform boundary earthquakes commonly occur in this area. Subduction zone earthquakes occur when one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, resulting in intense seismic activity. Transform boundary earthquakes, on the other hand, occur where two plates slide past each other horizontally. The San Andreas Fault, a significant transform boundary, is particularly renowned for its seismic activity in this region.
Among the notable earthquakes in this region, the San Francisco earthquake of 1906 stands out. This devastating earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 7.9, caused widespread destruction and loss of life. Additionally, the Cascadia Subduction Zone, stretching from northern California to southern British Columbia, is a source of concern due to the potential for a powerful megathrust earthquake.
In terms of geologic hazards beyond earthquakes, volcanic activity is also prominent in the region. Several volcanoes, including Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier in Washington, have erupted in the past and continue to be closely monitored for potential volcanic hazards.
Given the intense seismic activity in this region, it is crucial for stakeholders, including governments, communities, and individuals, to be prepared for earthquakes and volcanic events. Seismic monitoring, early warning systems, and strict building codes have been established to mitigate the impact of seismic events. Ongoing research and preparedness efforts continue to be important in managing the seismic risks posed by this region.
Potential Hazards and Dangers from the Recent Earthquake near Amahai, Maluku, Indonesia: Assessing Future Risks and Relevant Information
Recent Earthquake Strikes Amahai, Maluku, Indonesia
Amahai, Maluku, Indonesia – A recent earthquake with a magnitude of struck the town of Amahai on [date]. The epicenter of the earthquake was located in San Francisco, Indonesia. Fortunately, there have been no reports of damage, injuries, or other impacts resulting from the seismic event.
Although the earthquake was felt across the town, its impact remained limited due to its relatively low magnitude. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), earthquakes with magnitudes below 3.0 are typically not noticeable by people and do not cause significant damage. This event serves as a reminder for residents to be prepared for the possibility of larger earthquakes in the future.
The authorities and local emergency response teams have been on standby and continue to monitor the situation closely. As of now, there are no immediate concerns regarding aftershocks or other potential consequences caused by the earthquake. However, it is crucial for residents to remain vigilant and prepared for any unexpected developments.
It is important to note that the occurrence of earthquakes is relatively common in this region due to its location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for its intense tectonic activity. Therefore, it is always advisable for residents to have emergency kits in place, disaster preparedness plans, and to stay informed about safety measures.
We will continue to provide updates on the situation in Amahai as more information becomes available.
Earthquake Resources for the Affected
- Indonesia National Board for Disaster Management (BNPB): Official government agency responsible for managing and coordinating disaster response in Indonesia.
- Amahai Regional Government: Local government body likely to provide information on emergency services, shelters, and relief efforts specific to the affected area.
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA): Offers coordination and support mechanisms to assist countries in responding to humanitarian crises.
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC): Humanitarian organization providing emergency assistance, including medical support, shelter, and relief supplies.
- Indonesian Red Cross Society (PMI): Local chapter of the International Red Cross Society, providing immediate assistance, medical aid, and support in disaster situations.
- US Geological Survey (USGS): Provides real-time earthquake data, maps, and scientific information to understand the earthquake’s intensity, depth, and potential aftershocks.
- World Health Organization (WHO): International agency offering guidance on healthcare services, epidemic response, and emergency medical support during disasters.
- Google Crisis Response: Google’s crisis response page aggregates emergency information, maps, emergency contact numbers, and news updates during disasters.
- Facebook Safety Check: Facebook’s Safety Check feature allows individuals to mark themselves as safe, helping friends and family know they are unharmed during a crisis.
- Twitter: Information and updates can often be found by monitoring relevant hashtags and accounts related to earthquake response and relief efforts.